前言
大家都可能都在自己的应用中集成Crash收集服务,通常使用NSSetUncaughtExceptionHandler() + signal() / sigaction()的方式。它可以帮助我们收集到大部分Crash,直到后来发现stack overflow并不能被以上方法扑捉到,而且其它一些SDK也未能收集。那这篇文章简单介绍下Mach异常与signal的联系。
OS X 、iOS系统架构
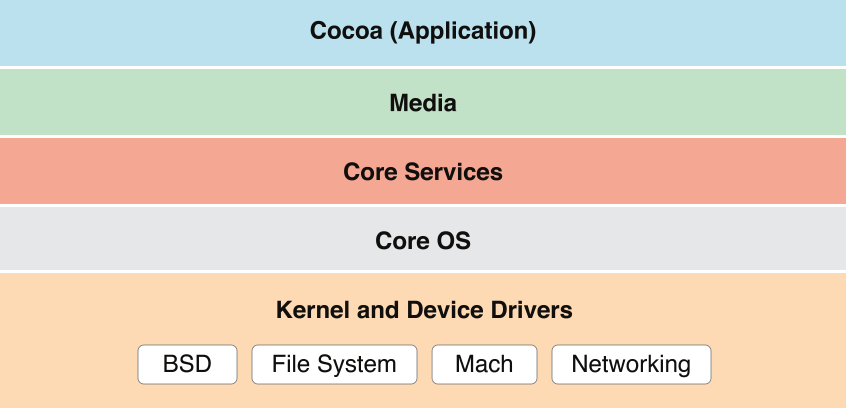
这张图片来之苹果Mac Technology Overview,除了用户体验层,OS X与iOS架构大体上是一直的。它们内核核心都是XNU(包含Mach、BSD)。Mach是微内核,负责操作系统中基本职责:进程和线程抽象、虚拟内存管理、任务调度、进程间通信和消息传递机制。BSD层简历在Mach上,提供一套可靠且更现代的API,提供了POSIX兼容性。
本文用到的XNU的版本号为3248.60.10的源码,下载地址。
你也可以在http://opensource.apple.com 中下载历史版本。
Mach exceptions 与 POSIX signals
Exception Type项通常会包含两个元素: Mach异常 和 Unix信号。
Mach exceptions: 允许在进程里或进程外处理,处理程序通过Mach RPC调用。
POSIX signals: 只在进程中处理,处理程序总是在发生错误的线程上调用。
Mach
异常首先是由处理器陷阱引发的。 通用的Mach异常处理程序exception_triage(),负责将异常转换成Mach 消息。exception_triage()通过调用exception_deliver()尝试把异常投递到thread、task最后是host。首先尝试将异常抛给thread端口,然后尝试抛给task端口,最后再抛给host端口(默认端口),如果没有一个端口返回KERN_SUCCESS,那么任务就会被终止。
|
|
异常行为
|
|
|
|
BSD
当第一个BSD进程调用bsdinit_task()函数启动时,这函数还调用了ux_handler_init()函数设置了一个Mach内核线程跑ux_handler()的。
|
|
|
|
|
|
每一个thread、task及host自身都有一个异常端口数组,通过调用xxx_set_exception_ports()(xxx为thread、task或host)可以设置这些异常端口。 xxx_set_exception_ports()第四个参数为exception_behavior_t behavior,这将会使用到与行为相匹配的实现(exc.defs 或 machexc.defs)。
各种行为都在host层被catch[mach]_exception_xxx处理,64位的对应的是有mach函数(可在/bsd/uxkern/ux_exception.c查看)。
这些函数通过调用ux_exception()将异常转换为对应的UNIX信号,并通过threadsignal()将信号投递到出错线程。
|
|
所以,如果异常是栈溢出,那么signal是SIGSEGV而不是SIGBUS;如果进程退出了或者线程/进程未准备好处理signal,所注册的signal()是无法接收信号的。
|
|
把Mach exception 和 UNIX signal 的转换制表后,如下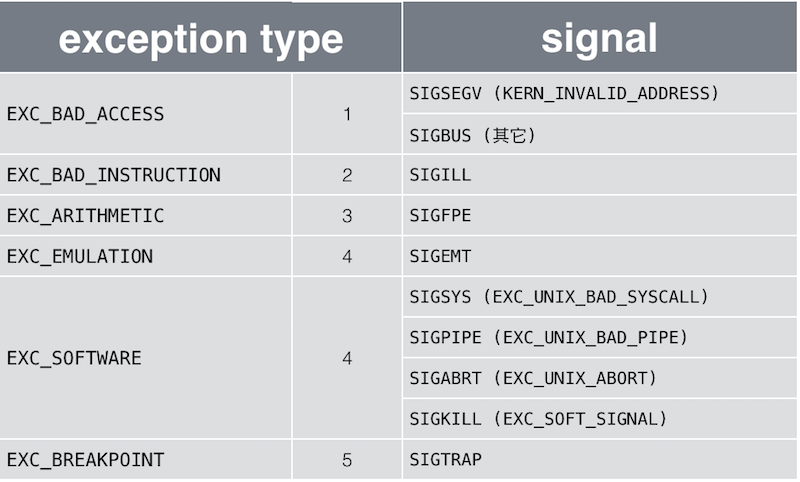
用下图来展示而Mach exception转换成signal的流程(图截自 Mac OS X and iOS Internals)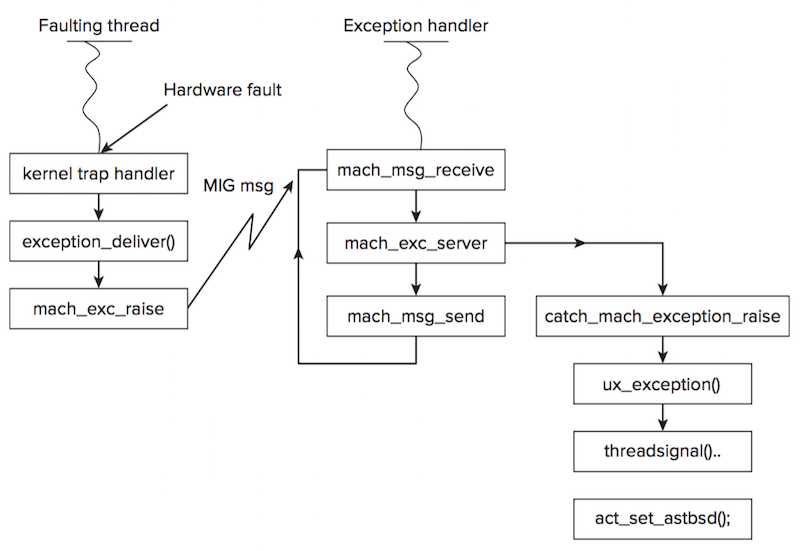
实践
在Mach中,异常是通过内核中的主要设施-消息传递机制-进行处理的。一个异常与一条消息并无差别,由出错的线程或任务(通过 msg_send())发送,并通过一个处理程(通过 msg_recv())接收。
由于Mach的异常以消息机制处理而不是通过函数调用,exception messages可以被转发到先前注册的Mach exception处理程序。这意味着你可以插入一个exception处理程序,而不干扰现有的无论是调试器或Apple’s crash reporter。可以使用mach_msg() // flag MACH_SEND_MSG发送原始消息到以前注册的处理程序的Mach端口,将消息转发到一个现有的处理程序。
知道以上这些,那我们来尝试扑捉一下Mach异常
|
|
接下来,我们测试一下。
|
|
调用这个方法,结果如下
Exc handler listening
Got message 2401. Exception : 1 Flavor: 0. Code 2/1486065656. State count is 8
(lldb)
我们可以查看mach/exception_types.h 对exception type的定义
Exception: 1 ,即为EXC_BAD_ACCESS
code: 2,即KERN_PROTECTION_FAILURE
而ux_exception() 函数告诉我们Code与signal是怎么转换的。
也就是 Exception = EXC_BAD_ACCESS, code = 2 对应的是SIGBUS信号,又因为为是stack overflow,信号应该是SIGSEGV。
那么结这个exception就是:
Exception Type: EXC_BAD_ACCESS (SIGSEGV)
Exception Subtype: KERN_PROTECTION_FAILURE
再试试其它的:
Exc handler listening
Got message 2401. Exception : 1 Flavor: 0. Code 1/4369. State count is 8
(lldb)Exception Type: EXC_BAD_ACCESS (SIGSEGV)
Exception Subtype: KERN_INVALID_ADDRESS
最后
除了上面硬件产生的信号,另外还有软件产生的信号。软件产生的信号来自kill()、pthread_kill()两个函数的调用,大概过程是这样的:kill()/pthread_kill() –> ... –> psignal_internal() –> act_set_astbsd()。最终也会调用act_set_astbsd()发送信号到目标线程。这意味着Mach exception流程是不会走的。
另外,在abort()源码注释着:<rdar://problem/7397932> abort() should call pthread_kill to deliver a signal to the aborting thread , 它是这样调用的(void)pthread_kill(pthread_self(), SIGABRT);。Apple’s Crash Reporter 把SIGABRT的Mach exception type记为EXC_CRASH,不同与上面转变表。
Exception Type: EXC_CRASH (SIGABRT)
Exception Codes: 0x0000000000000000, 0x0000000000000000
所以尽管Mach exception handle 比 UNIX signal handle 更有优势,但我们还是须要注册signal handle用于处理EXC_SOFTWARE/EXC_CRASH。
由于篇幅有限,有些细节可能并没有展现出来,如果你想有深入的了解,可以阅读下面参考文献,或者一些开源框架。最后,希望这篇文章可以帮助你了解Mach exception。
参考文献:
Apple Kernel Programming Guide
漫谈iOS Crash收集框架)
Mac OS X and iOS Internals:To the Apple’s Core(中文译名:深入解析 MAC OS X & IOS 操作系统)
Mach Exception Handlers
xnu-3248.60.10.tar.gz
Understanding Crash Reports on iPhone OS(wwdc)
Understanding and Analyzing iOS Application Crash Reports